o What three factors should be considered when designing an image acquisition plan?
The three factors that should be considered when making an image acquisition plan are the type of terrain or object that will be reconstructed, the ground sampling distance (GSD), and the overlap need for the terrain.
o Type Image Acquisition in the search. What does this article cover?
This article mostly covers the different flight patterns to use when a in the situation for it, but these are talked about to reinforce the main topic of overlap. Overlap is important to fully collect the needed data.
o Type minimum overlap. Then read the ‘how to verify that there is enough overlap between the images’.
§ What is general bare minimum for overlap front and side
The bare minimum for overlap varies on the terrain. In the general case, it is recommended the minimum overlap to be 75% frontal and 60% side overlap.
§ What is it for dense forest? Why do you suppose the increased need?
For forests, or dense areas with vegetation, it is recommended for a minimum 85% frontal and 70% side overlap.
o Type orthomosaic into the search. Then read the article on photo stitching vs. Orthomosaic generation. What is the difference?
The difference between photo stitching and orthomosaic generation are the amount of connections needed, and the dataset capability. Photo stitching requires less than 100 matches to glue together an image, it is recommended for small datasets and flat areas. Orthomosaics require more matches than photo stitching with 1000 matches. These matches however can be used on any terrain, while creating distances that can be used for measurements later. Orthos are used for large datasets as well.
o Type merge projects. When is merging projects useful?
Merging projects together is useful when image acquisition types are used, and when the dataset is considered large for the capabilities of the available processing resources.
o What is the difference between a global and linear rolling Shutter?
The difference between a global and linear rolling shutter is that a global captures the picture all in one frame and a rolling shutter captures the picture in a progressive motion. When using rolling shutter on a surface, the final product appears as like a blanket laid over the surface.
o Are GCPs necessary for Pix4D? When are they highly recommended?
Pix4D does not need GCPs but are highly recommended when accuracy is paramount.
o What is the quality report?
The quality report is the report that displays possible errors and explains the overall quality of the project, as well as how well Pix4D created it.
Part 3: Use the software
When the analysis finished, many reports proceeded displaying the quality of the data set. The first report of the initial processing displayed the initial quality of the data provided, and whether or not the data will work to create a DSM. If there are caution signs displayed this could be that a couple images are bad and will not calibrate, so to fix this you can enter the menu of the images and remove the ones that will not calibrate. The software then displays a glimpse of what the final DSM will appear as. After the final processing is finished, Pix4D posts more quality reports describing the DSM that has been processed. Details describing the quality of the DSM and orthomosaic final product, Details of the point cloud declassification, and the point cloud mesh quotes (displayed below) are all provided for you in the final report. After the report is read through, and problems have been corrected, Pix4D provides a DSM with missing parts of the surface. This is due to not enough overlap within the data, so those portions did not make the final product. After the orthomosaic was created a 'fly by' video was recorded to demonstrate the contours and features of the Pix4D product. The video is provided in the URL link below.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w_G-c0cgfN8
Part 4: Maps
o Shaded DSM
| Lab #3 Hillshade DSM |
o Orthomosaic
Part 5: Report
o Introduction: basic overview of software
Pix4D is a software that takes UAS collected data and analysis it for eligibility to stitch together a DSM. This software is important to processing UAS data because it is capable of connecting points and images to create fairly accurate and detailed 3D models of the terrain, wether it be for DSMs, DEMs, or DTMs. For this lab's particular data set, which was provided, there were no GCPs so the DSM did not connect all of the provided images. This caused empty spaces within the DSM, and can be seen in the video. Rolling shutter was used to create the overlap. This caused a blanket like coverage in the DSM terrain, observed from the distortion of the vehicles at the bottom of the DSM. Software like Pix4D is important due to its accuracy for this industry, but depending on the size of the dataset and the settings selected the process can be time consuming. Processing time can be the major portion of the time spent on a project. For lab #4 the processing time can be seen below.
o Conclusions: final critique.
As was said above, software like Pix4D is important to the UAS geospatial industry. It provides the easiest, one of the cheapest, and most accurate way of collecting and analyzing geospatial data. Pix4D specifically provides a software that is easy to use, and very accurate. It may be one of the fastest processes, but it still takes quite a bit of time. This is a drawback especially if you do not possess a fast enough computer to process the data. Pix4D will bog down the computer so much that it will be hard to do other things with a normal computer. Another drawback is if the data does not provide a sufficient enough overlap, then the whole time collecting the data in the field would have been a waste. Otherwise the software used in this lab seemed to be fairly easy to use, and I am looking forward to use it again.
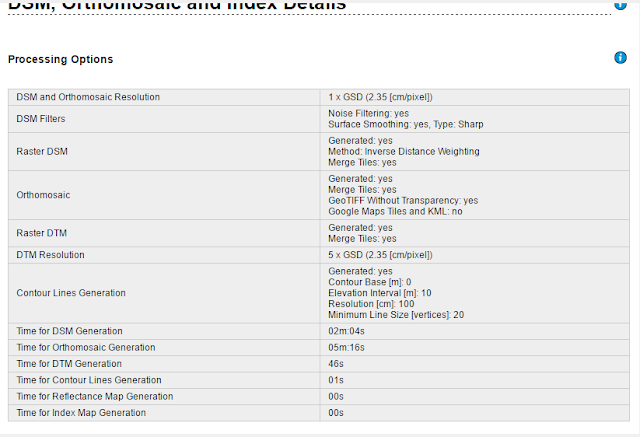 |
| DSM, Orthomosaic Details |
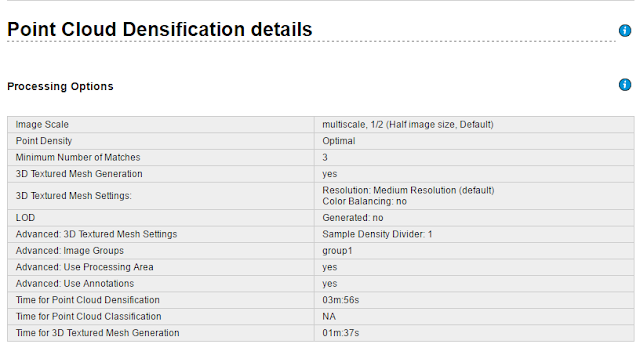 |
| Point Cloud Densification Details |
 |
| Quality Report |
 |
| Point Cloud Mesh Results |


No comments:
Post a Comment